LISA


It will become the first space observatory of gravitational waves (ESA/NASA)
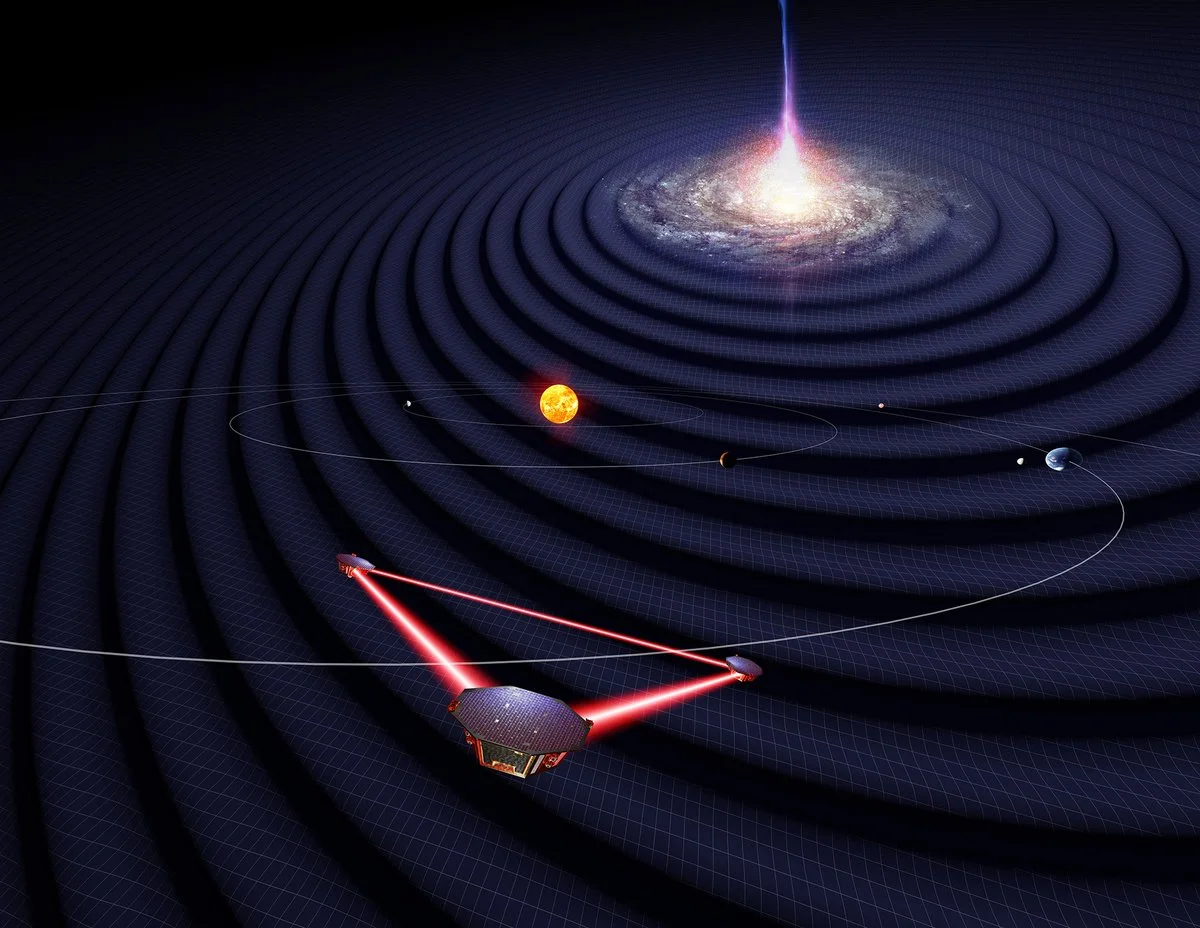
LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) is a European Space Agency (ESA) mission planned for 2035. The mission consists of three spacecraft millions of kilometres apart, tracking tens of millions of kilometres—more than a hundred times the distance to the Moon—behind the Earth as it orbits the Sun. The three probes emit laser beams from each other, and the signals are combined to look for signs of gravitational waves from space-time distortions.
This giant detector, larger than the Earth, will detect gravitational waves from orbiting black holes hundreds of millions of times more massive than the Sun.
Thanks to its all-sky capability, LISA will offer a broad view of a dynamic Cosmos using gravitational waves as new and unique messengers to unveil the gravitational Universe and will provide the closest view of the early Universe at TeV energy scales. The LISA mission will measure source parameters with astrophysically relevant sensitivity, from their smallest scale near black hole horizons, up to cosmological scales.
Acknowledgements: This work was (partially) supported by the Spanish MICIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by "ERDF A way of making Europe" by the European Union through grants PID2022-137674NB-I00, PID2019-106515-I00, ESP2017-90084-P (MINECO/FEDER, UE), ESP2015-67234-P (MINECO/FEDER, UE).
THE IEEC CONTRIBUTION
The IEEC leads the Spanish contribution to the LISA mission. More specifically, the Institute contributes with the Payload Control System, including software, and the Payload Diagnostic Package: sensors (and some actuators), thermal, magnetic, and radiation monitoring. In addition, the IEEC will have one of the Ground Segment Data Centres (the main Data Centre is located in Paris), which will allow local analysis of the actual data. This centre will represent an upgrade of the current LISA Pathfinder operations room, which is currently located at the ICE-CSIC facilities (on the UAB campus). Other similar data centres will be located in Germany, UK, and Italy.
The knowledge acquired during the LISA Pathfinder mission has provided a high-precision laser metrology system operating at low frequencies, which has great potential to play an important role during the development of the mission, in particular for testing the machinery developed by other institutes in collaboration with LISA.
TEAM
With the support of


